Table of Contents
- THC-A (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
- Delta-9-THC (d9-Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Delta-8-THC (d8- Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid)
- CBD (Cannabidiol)
- CBGA (Cannabigerolic Acid)
- CBG (Cannabigerol)
- CBN (Cannabinol)
- CBC (Cannabichromene)
- CBDV (Cannabidivarin)
- THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)
- Other cannabinoids

Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that are primarily found in the cannabis plant. They interact with the endocannabinoid system or ECS in the human body, which is involved in regulating various physiological processes. Some of the processes the ECS regulates are pain perception, Inflammation, appetite and metabolism, mood and emotions, sleep, memory and learning, motor control, cardiovascular function, reproductive processes, and immune function. Cannabinoids that are most commonly found in our flower, and extracts are CBGA, CBN, d9-THC, and THC-A. Cannabinoids that are found at low levels and less common in our products are CBDV, CBDA, CBD, CBC, CBG, d8-THC, and THCV. Below is a brief description of the effects of each cannabinoid we are able to quantify or measure in our analytical laboratory, as well as the products they can be found in.
THC-A (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
THC-A is the acidic precursor to d9-THC. It is non-psychoactive and typically found in higher concentrations in fresh cannabis plants. When heated, THC-A undergoes decarboxylation and converts into d9-THC, the well-known psychoactive compound. This occurs via heat from a lighter or another heating source to provide vaporization. Some therapeutic benefits of this cannabinoid are anti-inflammatory properties, and neuroprotective benefits (protection of nerve cells in the brain) beneficial for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. THC-A has shown anti-nausea and antiemetic (anti-vomiting) effects. This cannabinoid also presents antioxidant properties, preventing oxidative stress and associated health issues, and stimulates appetite as well. This is the most common cannabinoid in our flower, at high concentrations, with certain strains it has been measured as high as 35%. This is also found in many of our extracts (live resin, cured resin, rosin) at high concentrations of 50%-85%.
Delta-9-THC (d9-Tetrahydrocannabinol)
d9-THC is the most well-known and, aside from THC-A, the most abundant psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis. It is responsible for the “high” or euphoric effects associated with cannabis use. D9-THC has various therapeutic properties, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction. This cannabinoid is most commonly found in our distillate that is placed into our cartridges. The distillation process we practice uses heat that converts THC-A into d9-THC. D9-THC is also found in flower samples at low concentrations (0.10% to 2%), THC-A being at a higher concentration. This is why “total THC” is calculated, using the molecular weight difference of the two cannabinoids to calculate the overall percentage of both cannabinoids combined.
Delta-8-THC (d8- Tetrahydrocannabinol)
d8-THC is an isomer of delta-9-THC. Delta-8 THC is known for its psychoactive properties, inducing milder and less potent effects when compared to delta-9-THC. Users often describe its effects as promoting relaxation, euphoria, and a more clear-headed high than that of delta-9 THC. Delta-8 THC also presents some therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, antiemetic effects (reducing nausea and vomiting), appetite stimulation, and anxiolytic effects (reducing anxiety).
CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid)
CBDA is the acidic form of CBD. Like THCA, it is non-psychoactive and commonly found in raw cannabis. CBDA has gained attention for its potential anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea, and potential anticancer properties. When heated, CBDA converts to CBD. CBDA is found in our flower and extracts at relatively low concentrations.
CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD is another major cannabinoid found in cannabis. Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t produce a euphoric effect. CBD has gained significant attention for its potential therapeutic benefits, including its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic, and antipsychotic properties. CBD is found in our flower, extracts, topicals, edibles, and 1:1 distillate cartridges.
CBGA (Cannabigerolic Acid)
CBGA is the acidic precursor to CBG. It is considered the “mother cannabinoid” because it serves as a precursor for the synthesis of other cannabinoids. CBGA has potential antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. Through enzymatic reactions, CBGA can be converted into THCA, CBDA, and other cannabinoids. CBGA can be found in our flower and extracts.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that acts as a precursor to other cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD. It is often found in lower concentrations compared to THC and CBD. CBG shows promise in various therapeutic applications, including as an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and potential neuroprotective agent. CBG is only found in our distillate that is flavored and placed into our cartridges.
CBN (Cannabinol)
CBN is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that is typically formed through the degradation of d9-THC. It is known for its sedative properties and is sometimes used as a sleep aid. CBN is believed to have potential antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and appetite-stimulating effects. CBN is found in our flower, extracts, and distillate.
CBC (Cannabichromene)
CBC is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid, meaning it does not produce the psychoactive effects associated with THC. It provides anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and neuroinflammatory disorders. It also provides pain relief. CBC also can potentially benefit conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders. Research also indicates that CBC, along with other cannabinoids, possess anti-cancer properties. CBC may have an impact on mood and mental health, as evidence suggests that it may have antidepressant properties, as it interacts with neural pathways involved in mood regulation. CBC is typically found in our flower and extracts.
CBDV (Cannabidivarin)
CBDV is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis. Research has noted that CBDV has many potential therapeutic benefits. Some of which being: Anticonvulsant (anti-seizure) properties, anti-inflammatory effects, anti-nausea properties, and potential anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties. CBDV is typically found in our tincture.
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)
THCV is generally considered non-psychoactive, although it can produce mild psychoactive effects at higher doses. Like CBDV, and most cannabinoids; THCV affects the human body in many ways. Some of the effects it presents in the human body are as follows: Appetite suppression, neuroprotective properties as it has shown a potential therapeutic application for Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, it has anticonvulsant (anti-seizure) effects. THCV is found in our flower. We have found that it is more commonly found when cannabis is grown indoors rather than outdoors or in a greenhouse.
Other cannabinoids
There are over 100 known cannabinoids in cannabis, each with its own unique properties and potential therapeutic applications. Many of these cannabinoids have yet to be studied. It should also be stated that research on these cannabinoids is limited, and the therapeutic benefits of each need further exploration and clinical validation. Additionally, the effects of these cannabinoids vary depending on dosage, individual and genetic differences, and interactions with other compounds present in the cannabis plant. Always consult with a healthcare professional before considering any cannabis-derived products for medical purposes.
More Reading
A Day in the Life of Analytical Scientist Jeremy Brown In the ever-evolving world of cannabis science, a silent hero [...]
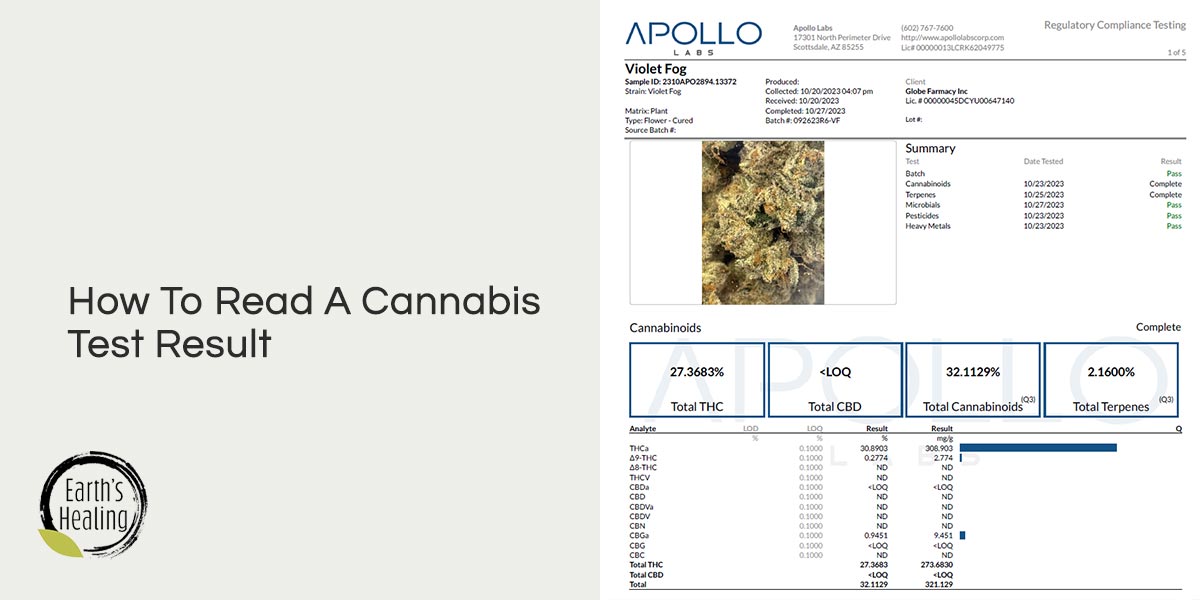
Laboratory Information Look for details about the laboratory that performed the analysis. This includes the lab's name, address, contact [...]
Terpenes are chemical compounds that are produced by a wide array of plants and animals. They make up the [...]