Laboratory Information
Look for details about the laboratory that performed the analysis. This includes the lab’s name, address, contact information, accreditation, and certification.
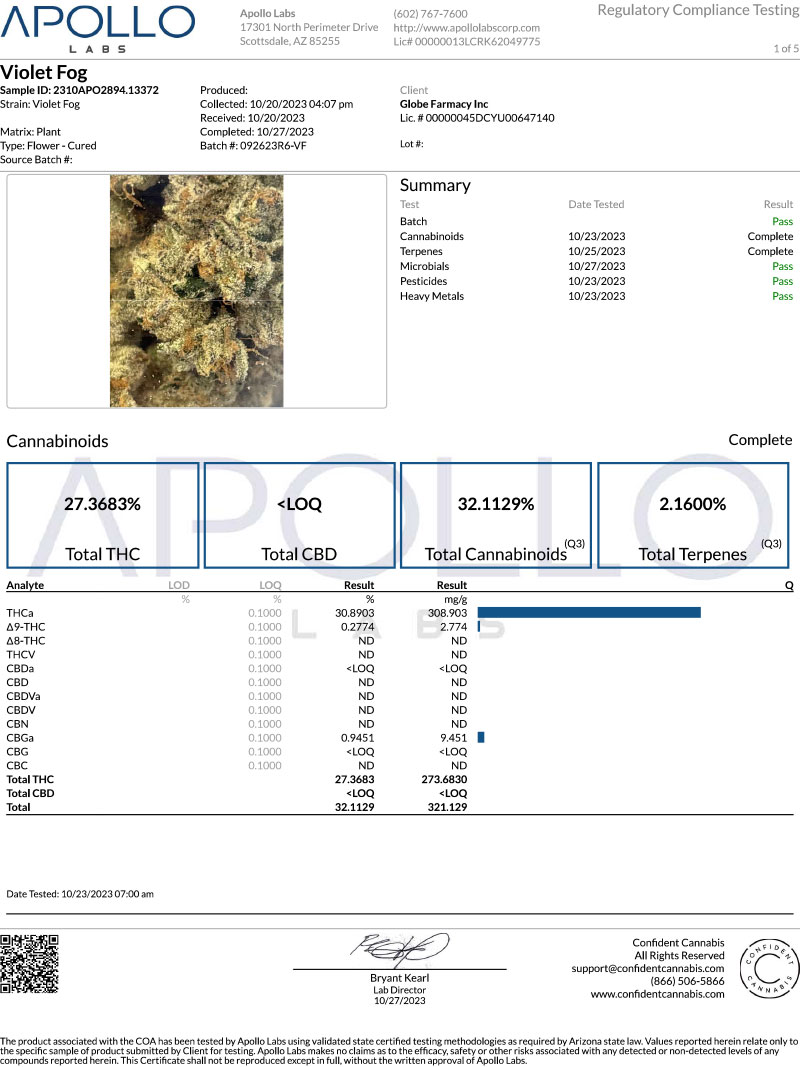
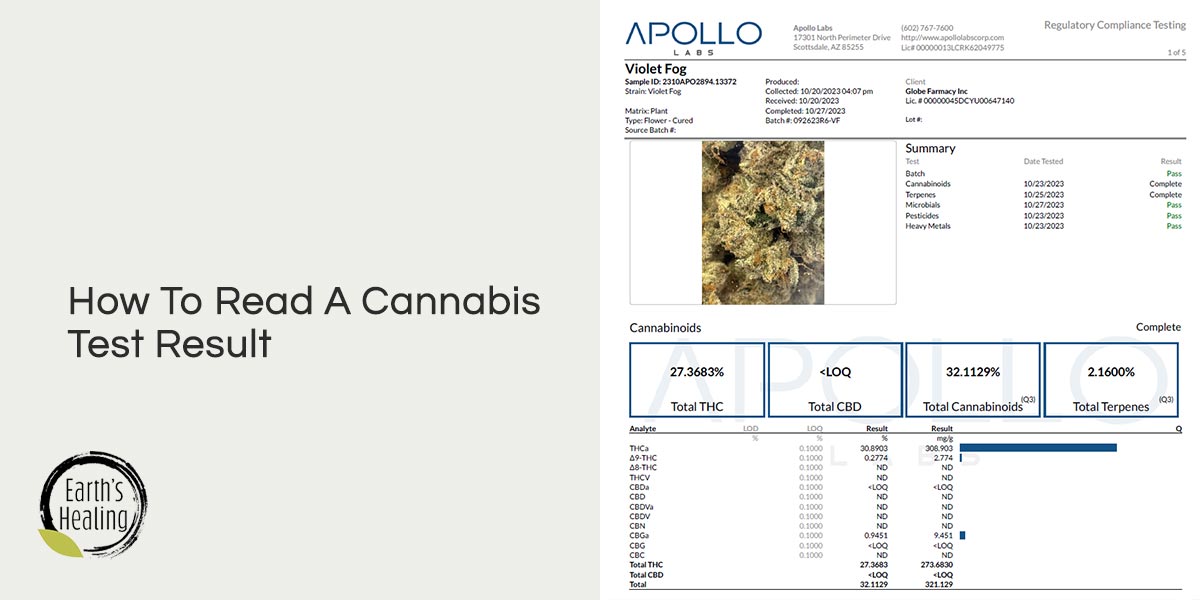
Sample Information
The CoA should specify the sample name or identification number, batch or lot number, and the date the laboratory received the sample.
Cannabinoid Profile
The cannabinoid profile section provides information about the levels of various cannabinoids present in the tested sample. It typically includes THC, CBD, and sometimes other cannabinoids like CBG, CBN, and CBC. The results are usually presented as percentages or milligrams per gram (mg/g) of the sample.
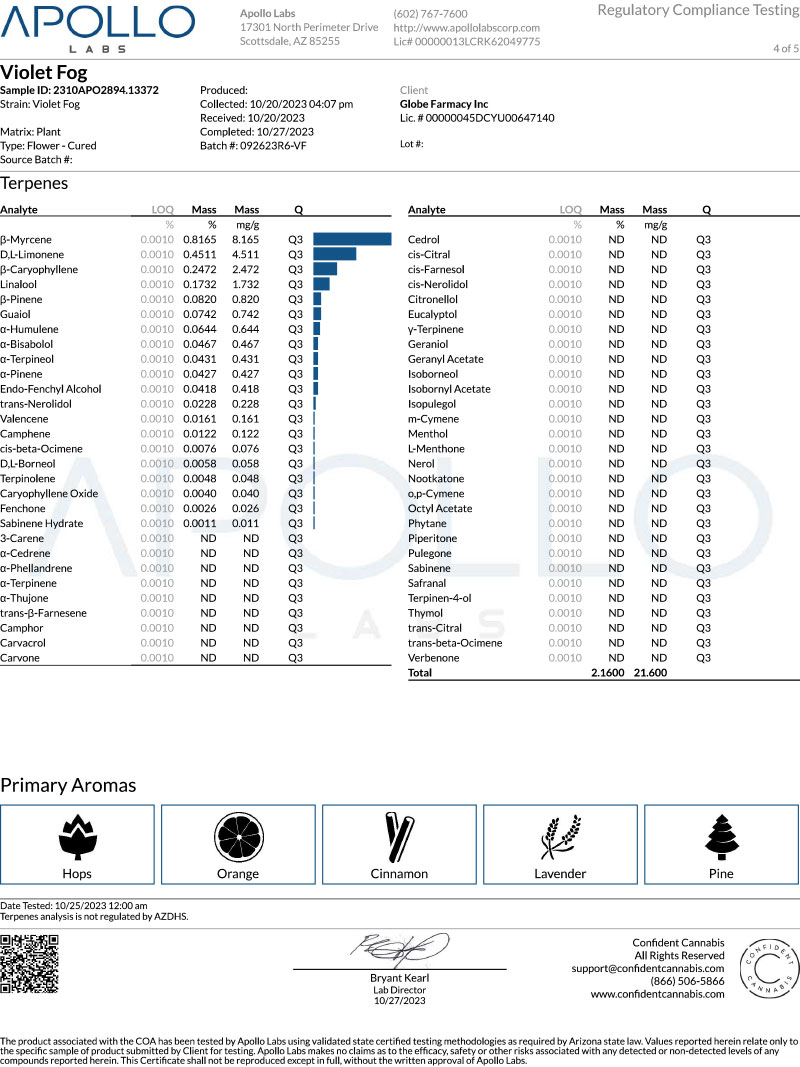
Terpene Profile
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in cannabis that contribute to its flavor and aroma. The CoA may include a terpene profile, listing the different terpenes detected in the sample and their corresponding concentrations. This information can help determine the potential effects and flavor profile of the strain or product.
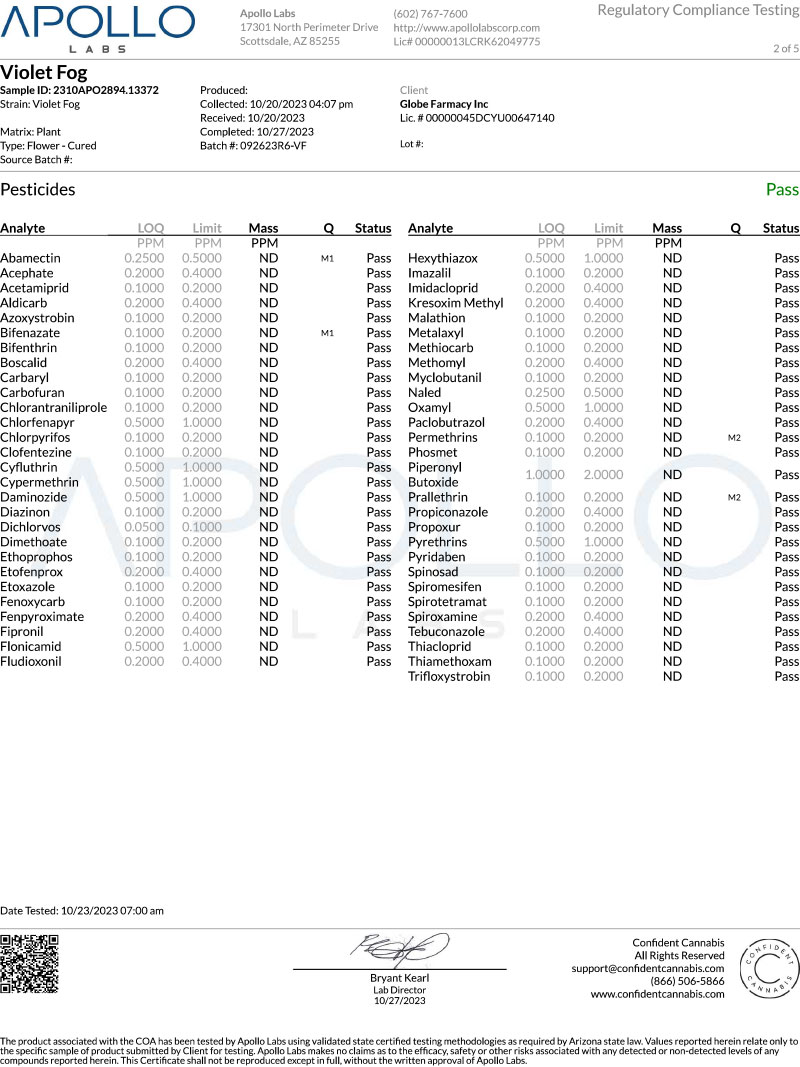
Pesticide Analysis
This section lists the pesticides tested for and their detection limits. It indicates whether any pesticides were found and, if so, whether they are within acceptable limits set by regulatory authorities. Low or non-detectable levels of pesticides are desirable for safety reasons.
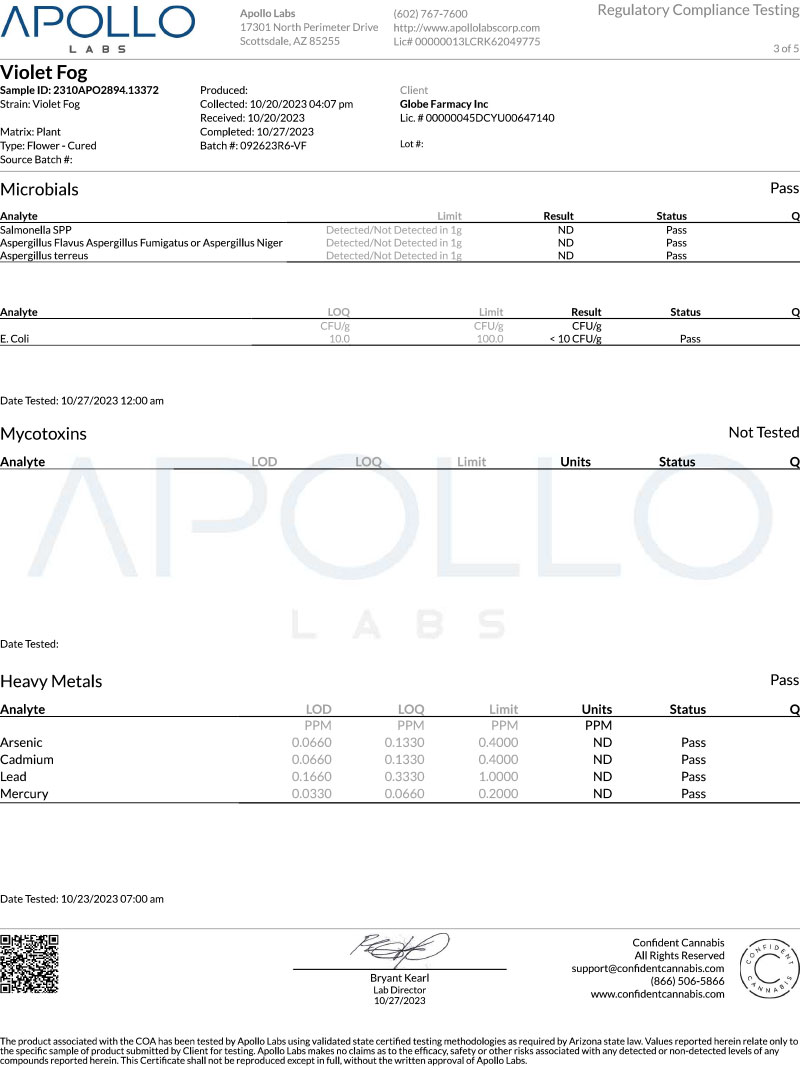
Microbial Analysis
The microbial analysis section assesses the presence of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and mold. It should indicate whether the sample passed or failed the microbial tests, ensuring that the product is free from harmful contaminants.
Heavy Metals
Heavy metal testing checks for the presence of toxic metals such as arsenic, lead, cadmium, and mercury. The CoA should indicate whether the sample passed the heavy metal tests or if any metals were detected above the permitted levels.
Residual Solvents
If the product was processed using solvents, such as butane or ethanol, the CoA may include a residual solvent analysis. It identifies the presence and levels of any residual solvents, ensuring that they are within safe limits.
Moisture Content
The moisture content section measures the amount of water in the sample. It is important because excessive moisture can promote the growth of mold and other contaminants. The CoA should specify the moisture content and indicate if it falls within acceptable ranges.
LOD (Limit of Detection)
LOD is the lowest concentration or amount of a specific compound that can be reliably detected by an analytical testing method. It represents the point at which the presence of the compound can be distinguished from background noise with a certain degree of confidence. In cannabis testing, LOD is an essential parameter to determine the sensitivity of the testing method for detecting trace amounts of various cannabinoids, terpenes, or contaminants in a sample.
LOQ (Limit of Quantification)
LOQ is the lowest concentration or amount of a specific compound that can be accurately and precisely quantified by an analytical testing method. Unlike the LOD, which only focuses on detection, the LOQ provides information on the level at which the compound can be measured and reported with a reasonable level of accuracy and precision. In cannabis testing, the LOQ is critical for determining the lowest concentration of a compound that can be reliably reported in a sample, ensuring the accuracy of potency and safety assessments.
Other Tests
Depending on the product and regulatory requirements, the CoA may include additional tests such as mycotoxin analysis, foreign matter inspection, or specific quality parameters.
More Reading
A Day in the Life of Analytical Scientist Jeremy Brown In the ever-evolving world of cannabis science, a silent hero [...]
Terpenes are chemical compounds that are produced by a wide array of plants and animals. They make up the [...]
Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that are primarily found in the cannabis plant. They interact with the [...]